SQL Tutorial SELECT Statement Extended Query Capabilities This subsection details the remaining features of SELECT statements. The basics are at SELECT Statement. UPDATE Transact SQL Microsoft Docs. ESTE TEMA SE APLICA A SQL Server a partir de 2. Azure SQL Database. Azure SQL Data Warehouse Almacenamiento de datos paralelos THIS TOPIC APPLIES TO SQL Server starting with 2. Query2-Design.jpg' alt='Update Sql From Table Joining' title='Update Sql From Table Joining' />Azure SQL Database. Azure SQL Data Warehouse Parallel Data Warehouse Cambia los datos de una tabla o vista de SQL Server 2. SQL Server 2. 01. Changes existing data in a table or view in SQL Server 2. SQL Server 2. 01. Para obtener ejemplos, vea ejemplos. For examples, see Examples. Convenciones de sintaxis de Transact SQLTransact SQL Syntax Conventions. Sintaxis. Syntax Syntax for SQL Server and Azure SQL Database. WITH lt commontableexpression. TOP expression PERCENT. WITH lt TableHintLimited. DEFAULT NULL. 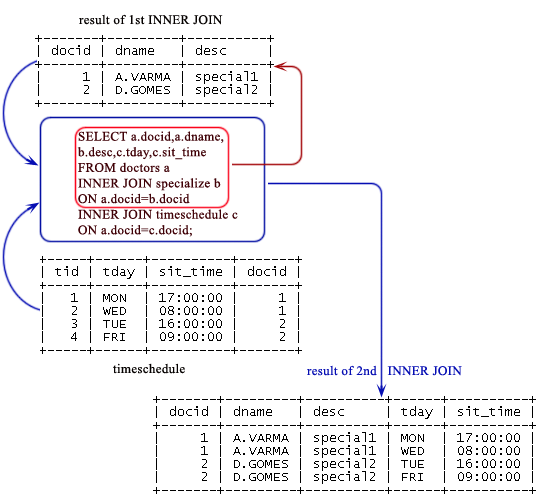 WRITE expression, Offset, Length. OUTPUT Clause. FROM lt tablesource. WHERE lt searchcondition. HTPictures/635647459804844742.JPG' alt='Update Sql From Table Joining' title='Update Sql From Table Joining' />CURRENT OF. GLOBAL cursorname. OPTION lt queryhint. Syntax for Azure SQL Data Warehouse and Parallel Data Warehouse. UPDATE databasename. SET columnname expression NULL. FROM fromclause. WHERE lt searchcondition. OPTION LABEL labelname. Argumentos. Arguments. CON lt commontableexpression WITH lt commontableexpression Especifica la vista o el conjunto de resultados temporal indicado, que tambin se conoce como expresin de tabla comn CTE, definido en el mbito de la instruccin UPDATE. Specifies the temporary named result set or view, also known as common table expression CTE, defined within the scope of the UPDATE statement. El conjunto de resultados CTE se deriva de una consulta simple. La instruccin UPDATE hace referencia al conjunto de resultados. The CTE result set is derived from a simple query and is referenced by UPDATE statement. Las expresiones de tabla comunes tambin se pueden utilizar con las instrucciones SELECT, INSERT, DELETE y CREATE VIEW. Common table expressions can also be used with the SELECT, INSERT, DELETE, and CREATE VIEW statements. Para obtener ms informacin, consulte con commontableexpression Transact SQL. For more information, see WITH commontableexpression Transact SQL. Parte superior expresin TOP expression PERCENT Especifica el nmero o porcentaje de filas que se actualizan. Specifies the number or percent of rows that are updated. Las filas a las que se hace referencia en la expresin TOP utilizada con INSERT, UPDATE o DELETE no se ordenan. Changes existing data in a table or view in SQL Server 2017. For examples, see Examples. Specifies the temporary named result set or view, also known as common table. The rows referenced in the TOP expression used with INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE are not arranged in any order. Utilizar parntesis para delimitar expresin en la parte superior se requieren en instrucciones INSERT, UPDATE y DELETE. Parentheses delimiting expression in TOP are required in INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE statements. Para obtener ms informacin, vea TOP Transact SQL. For more information, see TOP Transact SQL. Tablatablealias. Alias especificado en la clusula FROM que representa la tabla o vista de la que se van a actualizar las filas. The alias specified in the FROM clause representing the table or view from which the rows are to be updated. Es el nombre del servidor con un nombre de servidor vinculado o OPENDATASOURCE funcionar como el nombre del servidor en el que se encuentra la tabla o vista. Is the name of the server using a linked server name or the OPENDATASOURCE function as the server name on which the table or view is located. Si nombreservidor se especifica, databasename y schemaname son necesarios. If servername is specified, databasename and schemaname are required. Es el nombre de la base de datos. Is the name of the database. Es el nombre del esquema al que pertenece la tabla o la vista. Is the name of the schema to which the table or view belongs. Es el nombre de la tabla o vista cuyas filas se deben actualizar. Is the name of the table or view from which the rows are to be updated. La vista hace referencia a nombretablaovista debe ser actualizable y referencia exactamente a una tabla base en la clusula FROM de la vista. The view referenced by tableorviewname must be updatable and reference exactly one base table in the FROM clause of the view. Para obtener ms informacin acerca de las vistas actualizables, vea CREATE VIEW Transact SQL. For more information about updatable views, see CREATE VIEW Transact SQL. Conjunto. Filas. Limitadorowsetfunctionlimited. Es el OPENQUERY o OPENROWSET funcin, dependiendo del proveedor. Is either the OPENQUERY or OPENROWSET function, subject to provider capabilities. CON lt sugerencia. Tabla. Limitada WITH lt TableHintLimited Especifica una o varias sugerencias de tabla que estn permitidas en una tabla de destino. Specifies one or more table hints that are allowed for a target table. La palabra clave WITH y los parntesis son obligatorios. The WITH keyword and the parentheses are required. No se permiten NOLOCK ni READUNCOMMITTED. NOLOCK and READUNCOMMITTED are not allowed. Para obtener informacin acerca de las sugerencias de tabla, vea sugerencias de tabla Transact SQL. For information about table hints, see Table Hints Transact SQL. Especifica un tabla variable como una tabla de origen. Specifies a table variable as a table source. SETSETEspecifica la lista de nombres de variable o de columna que se van a actualizar. Specifies the list of column or variable names to be updated. Es una columna que contiene los datos que se van a cambiar. Is a column that contains the data to be changed. Las columnas de identidad no se pueden actualizar. Identity columns cannot be updated. Es una variable, un valor literal, una expresin o una instruccin de subseleccin entre parntesis que devuelve un solo valor. Is a variable, literal value, expression, or a subselect statement enclosed with parentheses that returns a single value. El valor devuelto por expresin reemplaza al valor existente en columnname o variable. The value returned by expression replaces the existing value in columnname or variable. Nota. Al hacer referencia a los tipos de datos de caracteres Unicode nchar, nvarchar, y ntext, expression debe agregarse como prefijo la letra mayscula n. When referencing the Unicode character data types nchar, nvarchar, and ntext, expression should be prefixed with the capital letter N. Si no se especifica N, SQL Server. SQL Server convierte la cadena a la pgina de cdigos que se corresponde con la intercalacin predeterminada de la base de datos o columna. If N is not specified, SQL Server. SQL Server converts the string to the code page that corresponds to the default collation of the database or column. Los caracteres que no se encuentren en esta pgina de cdigos se perdern. Any characters not found in this code page are lost. DEFAULTDEFAULTEspecifica que el valor predeterminado definido para la columna debe reemplazar al valor existente en esa columna. Specifies that the default value defined for the column is to replace the existing value in the column. Esta operacin tambin puede utilizarse para cambiar la columna a NULL si no tiene asignado ningn valor predeterminado y se ha definido para aceptar valores NULL. Join SQL Wikipedia. An SQLjoin clause combines columns from one or more tables in a relational database. It creates a set that can be saved as a table or used as it is. A JOIN is a means for combining columns from one self join or more tables by using values common to each. ANSI standard SQL specifies five types of JOIN INNER, LEFT OUTER, RIGHT OUTER, FULL OUTER and CROSS. As a special case, a table base table, view, or joined table can JOIN to itself in a self join. A programmer declares a JOIN statement to identify rows for joining. If the evaluated predicate is true, the combined row is then produced in the expected format, a row set or a temporary table. Sample tableseditRelational databases are usually normalized to eliminate duplication of information such as when entity types have one to many relationships. For example, a Department may be associated with a number of Employees. Joining separate tables for Department and Employee effectively creates another table which combines the information from both tables. All subsequent explanations on join types in this article make use of the following two tables. The rows in these tables serve to illustrate the effect of different types of joins and join predicates. In the following tables the Department. IDcolumn of the Department table which can be designated as Department. Department. ID is the primary key, while Employee. Department. ID is a foreign key. Employee table. Last. Name. Department. IDRafferty. 31. Jones. Heisenberg. 33. Robinson. Smith. 34. Williams. NULLDepartment table. Department. IDDepartment. Name. 31. Sales. 33. Engineering. 34. Clerical. Marketing. Note In the Employee table above, the employee Williams has not been assigned to any department yet. Also, note that no employees are assigned to the Marketing department. This is the SQL statement to create the aforementioned tables. CREATETABLEdepartment 2 3 Department. IDINTPrimarykey, 4 Department. Name. VARCHAR2. 0 5 6 7 CREATETABLEemployee 8 9 Last. Name. VARCHAR2. 0,1. Department. IDINTreferencesdepartmentDepartment. ID1. 1 1. 2 1. INSERTINTOdepartment. VALUES3. 1,Sales 1. INSERTINTOdepartment. VALUES3. 3,Engineering 1. INSERTINTOdepartment. VALUES3. 4,Clerical 1. INSERTINTOdepartment. VALUES3. 5,Marketing 1. INSERTINTOemployee. VALUESRafferty,3. INSERTINTOemployee. VALUESJones,3. INSERTINTOemployee. VALUESHeisenberg,3. INSERTINTOemployee. VALUESRobinson,3. INSERTINTOemployee. VALUESSmith,3. INSERTINTOemployee. VALUESWilliams,NULL Cross joineditCROSS JOIN returns the Cartesian product of rows from tables in the join. In other words, it will produce rows which combine each row from the first table with each row from the second table. Example of an explicit cross join SELECTFROMemployee. CROSSJOINdepartment Example of an implicit cross join SELECTROMemployee,department Employee. Last. Name. Employee. Department. IDDepartment. Department. Name. Department. Department. IDRafferty. 31. Sales. Jones. 33. Sales. Heisenberg. 33. Sales. Smith. 34. Sales. Robinson. 34. Sales. Ea Game Keygen Works 100 Download. Williams. NULLSales. Rafferty. 31. Engineering. Jones. 33. Engineering. Heisenberg. 33. Engineering. Smith. 34. Engineering. Robinson. 34. Engineering. Williams. NULLEngineering. Rafferty. 31. Clerical. Jones. 33. Clerical. Heisenberg. 33. Clerical. Smith. 34. Clerical. Robinson. 34. Clerical. Williams. NULLClerical. Rafferty. 31. Marketing. Jones. 33. Marketing. Heisenberg. 33. Marketing. Smith. 34. Marketing. Robinson. 34. Marketing. Williams. NULLMarketing. The cross join does not itself apply any predicate to filter rows from the joined table. The results of a cross join can be filtered by using a WHERE clause which may then produce the equivalent of an inner join. In the SQL 2. 01. F4. 01, Extended joined table, package. Normal uses are for checking the servers performance. Inner joinedit. A Venn Diagram representing an Inner Join SQL statement between the tables A and B. An inner join requires each row in the two joined tables to have matching column values, and is a commonly used join operation in applications but should not be assumed to be the best choice in all situations. Inner join creates a new result table by combining column values of two tables A and B based upon the join predicate. The query compares each row of A with each row of B to find all pairs of rows which satisfy the join predicate. When the join predicate is satisfied by matching non NULL values, column values for each matched pair of rows of A and B are combined into a result row. The result of the join can be defined as the outcome of first taking the Cartesian product or Cross join of all rows in the tables combining every row in table A with every row in table B and then returning all rows which satisfy the join predicate. Actual SQL implementations normally use other approaches, such as hash joins or sort merge joins, since computing the Cartesian product is slower and would often require a prohibitively large amount of memory to store. SQL specifies two different syntactical ways to express joins the explicit join notation and the implicit join notation. The implicit join notation is no longer considered a best practice, although database systems still support it. The explicit join notation uses the JOIN keyword, optionally preceded by the INNER keyword, to specify the table to join, and the ON keyword to specify the predicates for the join, as in the following example SELECTemployee. Last. Name,employee. Department. ID,department. Department. Name. FROMemployee. INNERJOINdepartment. ONemployee. Department. IDdepartment. Department. IDEmployee. Last. Name. Employee. Department. IDDepartment. Department. Name. Robinson. 34. Clerical. Jones. 33. Engineering. Smith. Clerical. Heisenberg. Engineering. Rafferty. Sales. The implicit join notation simply lists the tables for joining, in the FROM clause of the SELECT statement, using commas to separate them. Thus it specifies a cross join, and the WHERE clause may apply additional filter predicates which function comparably to the join predicates in the explicit notation. The following example is equivalent to the previous one, but this time using implicit join notation SELECTROMemployee,department. WHEREemployee. Department. IDdepartment. Department. ID The queries given in the examples above will join the Employee and Department tables using the Department. ID column of both tables. Where the Department. ID of these tables match i. Last. Name, Department. ID and Department. Name columns from the two tables into a result row. Where the Department. ID does not match, no result row is generated. Thus the result of the execution of the query above will be Employee. Last. Name. Employee. Department. IDDepartment. Department. Name. Department. Department. IDRobinson. 34. Clerical. Jones. 33. Engineering. Smith. 34. Clerical. Heisenberg. 33. Engineering. Rafferty. 31. Sales. The employee Williams and the department Marketing do not appear in the query execution results. Neither of these has any matching rows in the other respective table Williams has no associated department, and no employee has the department ID 3. Marketing. Depending on the desired results, this behavior may be a subtle bug, which can be avoided by replacing the inner join with an outer join.
WRITE expression, Offset, Length. OUTPUT Clause. FROM lt tablesource. WHERE lt searchcondition. HTPictures/635647459804844742.JPG' alt='Update Sql From Table Joining' title='Update Sql From Table Joining' />CURRENT OF. GLOBAL cursorname. OPTION lt queryhint. Syntax for Azure SQL Data Warehouse and Parallel Data Warehouse. UPDATE databasename. SET columnname expression NULL. FROM fromclause. WHERE lt searchcondition. OPTION LABEL labelname. Argumentos. Arguments. CON lt commontableexpression WITH lt commontableexpression Especifica la vista o el conjunto de resultados temporal indicado, que tambin se conoce como expresin de tabla comn CTE, definido en el mbito de la instruccin UPDATE. Specifies the temporary named result set or view, also known as common table expression CTE, defined within the scope of the UPDATE statement. El conjunto de resultados CTE se deriva de una consulta simple. La instruccin UPDATE hace referencia al conjunto de resultados. The CTE result set is derived from a simple query and is referenced by UPDATE statement. Las expresiones de tabla comunes tambin se pueden utilizar con las instrucciones SELECT, INSERT, DELETE y CREATE VIEW. Common table expressions can also be used with the SELECT, INSERT, DELETE, and CREATE VIEW statements. Para obtener ms informacin, consulte con commontableexpression Transact SQL. For more information, see WITH commontableexpression Transact SQL. Parte superior expresin TOP expression PERCENT Especifica el nmero o porcentaje de filas que se actualizan. Specifies the number or percent of rows that are updated. Las filas a las que se hace referencia en la expresin TOP utilizada con INSERT, UPDATE o DELETE no se ordenan. Changes existing data in a table or view in SQL Server 2017. For examples, see Examples. Specifies the temporary named result set or view, also known as common table. The rows referenced in the TOP expression used with INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE are not arranged in any order. Utilizar parntesis para delimitar expresin en la parte superior se requieren en instrucciones INSERT, UPDATE y DELETE. Parentheses delimiting expression in TOP are required in INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE statements. Para obtener ms informacin, vea TOP Transact SQL. For more information, see TOP Transact SQL. Tablatablealias. Alias especificado en la clusula FROM que representa la tabla o vista de la que se van a actualizar las filas. The alias specified in the FROM clause representing the table or view from which the rows are to be updated. Es el nombre del servidor con un nombre de servidor vinculado o OPENDATASOURCE funcionar como el nombre del servidor en el que se encuentra la tabla o vista. Is the name of the server using a linked server name or the OPENDATASOURCE function as the server name on which the table or view is located. Si nombreservidor se especifica, databasename y schemaname son necesarios. If servername is specified, databasename and schemaname are required. Es el nombre de la base de datos. Is the name of the database. Es el nombre del esquema al que pertenece la tabla o la vista. Is the name of the schema to which the table or view belongs. Es el nombre de la tabla o vista cuyas filas se deben actualizar. Is the name of the table or view from which the rows are to be updated. La vista hace referencia a nombretablaovista debe ser actualizable y referencia exactamente a una tabla base en la clusula FROM de la vista. The view referenced by tableorviewname must be updatable and reference exactly one base table in the FROM clause of the view. Para obtener ms informacin acerca de las vistas actualizables, vea CREATE VIEW Transact SQL. For more information about updatable views, see CREATE VIEW Transact SQL. Conjunto. Filas. Limitadorowsetfunctionlimited. Es el OPENQUERY o OPENROWSET funcin, dependiendo del proveedor. Is either the OPENQUERY or OPENROWSET function, subject to provider capabilities. CON lt sugerencia. Tabla. Limitada WITH lt TableHintLimited Especifica una o varias sugerencias de tabla que estn permitidas en una tabla de destino. Specifies one or more table hints that are allowed for a target table. La palabra clave WITH y los parntesis son obligatorios. The WITH keyword and the parentheses are required. No se permiten NOLOCK ni READUNCOMMITTED. NOLOCK and READUNCOMMITTED are not allowed. Para obtener informacin acerca de las sugerencias de tabla, vea sugerencias de tabla Transact SQL. For information about table hints, see Table Hints Transact SQL. Especifica un tabla variable como una tabla de origen. Specifies a table variable as a table source. SETSETEspecifica la lista de nombres de variable o de columna que se van a actualizar. Specifies the list of column or variable names to be updated. Es una columna que contiene los datos que se van a cambiar. Is a column that contains the data to be changed. Las columnas de identidad no se pueden actualizar. Identity columns cannot be updated. Es una variable, un valor literal, una expresin o una instruccin de subseleccin entre parntesis que devuelve un solo valor. Is a variable, literal value, expression, or a subselect statement enclosed with parentheses that returns a single value. El valor devuelto por expresin reemplaza al valor existente en columnname o variable. The value returned by expression replaces the existing value in columnname or variable. Nota. Al hacer referencia a los tipos de datos de caracteres Unicode nchar, nvarchar, y ntext, expression debe agregarse como prefijo la letra mayscula n. When referencing the Unicode character data types nchar, nvarchar, and ntext, expression should be prefixed with the capital letter N. Si no se especifica N, SQL Server. SQL Server convierte la cadena a la pgina de cdigos que se corresponde con la intercalacin predeterminada de la base de datos o columna. If N is not specified, SQL Server. SQL Server converts the string to the code page that corresponds to the default collation of the database or column. Los caracteres que no se encuentren en esta pgina de cdigos se perdern. Any characters not found in this code page are lost. DEFAULTDEFAULTEspecifica que el valor predeterminado definido para la columna debe reemplazar al valor existente en esa columna. Specifies that the default value defined for the column is to replace the existing value in the column. Esta operacin tambin puede utilizarse para cambiar la columna a NULL si no tiene asignado ningn valor predeterminado y se ha definido para aceptar valores NULL. Join SQL Wikipedia. An SQLjoin clause combines columns from one or more tables in a relational database. It creates a set that can be saved as a table or used as it is. A JOIN is a means for combining columns from one self join or more tables by using values common to each. ANSI standard SQL specifies five types of JOIN INNER, LEFT OUTER, RIGHT OUTER, FULL OUTER and CROSS. As a special case, a table base table, view, or joined table can JOIN to itself in a self join. A programmer declares a JOIN statement to identify rows for joining. If the evaluated predicate is true, the combined row is then produced in the expected format, a row set or a temporary table. Sample tableseditRelational databases are usually normalized to eliminate duplication of information such as when entity types have one to many relationships. For example, a Department may be associated with a number of Employees. Joining separate tables for Department and Employee effectively creates another table which combines the information from both tables. All subsequent explanations on join types in this article make use of the following two tables. The rows in these tables serve to illustrate the effect of different types of joins and join predicates. In the following tables the Department. IDcolumn of the Department table which can be designated as Department. Department. ID is the primary key, while Employee. Department. ID is a foreign key. Employee table. Last. Name. Department. IDRafferty. 31. Jones. Heisenberg. 33. Robinson. Smith. 34. Williams. NULLDepartment table. Department. IDDepartment. Name. 31. Sales. 33. Engineering. 34. Clerical. Marketing. Note In the Employee table above, the employee Williams has not been assigned to any department yet. Also, note that no employees are assigned to the Marketing department. This is the SQL statement to create the aforementioned tables. CREATETABLEdepartment 2 3 Department. IDINTPrimarykey, 4 Department. Name. VARCHAR2. 0 5 6 7 CREATETABLEemployee 8 9 Last. Name. VARCHAR2. 0,1. Department. IDINTreferencesdepartmentDepartment. ID1. 1 1. 2 1. INSERTINTOdepartment. VALUES3. 1,Sales 1. INSERTINTOdepartment. VALUES3. 3,Engineering 1. INSERTINTOdepartment. VALUES3. 4,Clerical 1. INSERTINTOdepartment. VALUES3. 5,Marketing 1. INSERTINTOemployee. VALUESRafferty,3. INSERTINTOemployee. VALUESJones,3. INSERTINTOemployee. VALUESHeisenberg,3. INSERTINTOemployee. VALUESRobinson,3. INSERTINTOemployee. VALUESSmith,3. INSERTINTOemployee. VALUESWilliams,NULL Cross joineditCROSS JOIN returns the Cartesian product of rows from tables in the join. In other words, it will produce rows which combine each row from the first table with each row from the second table. Example of an explicit cross join SELECTFROMemployee. CROSSJOINdepartment Example of an implicit cross join SELECTROMemployee,department Employee. Last. Name. Employee. Department. IDDepartment. Department. Name. Department. Department. IDRafferty. 31. Sales. Jones. 33. Sales. Heisenberg. 33. Sales. Smith. 34. Sales. Robinson. 34. Sales. Ea Game Keygen Works 100 Download. Williams. NULLSales. Rafferty. 31. Engineering. Jones. 33. Engineering. Heisenberg. 33. Engineering. Smith. 34. Engineering. Robinson. 34. Engineering. Williams. NULLEngineering. Rafferty. 31. Clerical. Jones. 33. Clerical. Heisenberg. 33. Clerical. Smith. 34. Clerical. Robinson. 34. Clerical. Williams. NULLClerical. Rafferty. 31. Marketing. Jones. 33. Marketing. Heisenberg. 33. Marketing. Smith. 34. Marketing. Robinson. 34. Marketing. Williams. NULLMarketing. The cross join does not itself apply any predicate to filter rows from the joined table. The results of a cross join can be filtered by using a WHERE clause which may then produce the equivalent of an inner join. In the SQL 2. 01. F4. 01, Extended joined table, package. Normal uses are for checking the servers performance. Inner joinedit. A Venn Diagram representing an Inner Join SQL statement between the tables A and B. An inner join requires each row in the two joined tables to have matching column values, and is a commonly used join operation in applications but should not be assumed to be the best choice in all situations. Inner join creates a new result table by combining column values of two tables A and B based upon the join predicate. The query compares each row of A with each row of B to find all pairs of rows which satisfy the join predicate. When the join predicate is satisfied by matching non NULL values, column values for each matched pair of rows of A and B are combined into a result row. The result of the join can be defined as the outcome of first taking the Cartesian product or Cross join of all rows in the tables combining every row in table A with every row in table B and then returning all rows which satisfy the join predicate. Actual SQL implementations normally use other approaches, such as hash joins or sort merge joins, since computing the Cartesian product is slower and would often require a prohibitively large amount of memory to store. SQL specifies two different syntactical ways to express joins the explicit join notation and the implicit join notation. The implicit join notation is no longer considered a best practice, although database systems still support it. The explicit join notation uses the JOIN keyword, optionally preceded by the INNER keyword, to specify the table to join, and the ON keyword to specify the predicates for the join, as in the following example SELECTemployee. Last. Name,employee. Department. ID,department. Department. Name. FROMemployee. INNERJOINdepartment. ONemployee. Department. IDdepartment. Department. IDEmployee. Last. Name. Employee. Department. IDDepartment. Department. Name. Robinson. 34. Clerical. Jones. 33. Engineering. Smith. Clerical. Heisenberg. Engineering. Rafferty. Sales. The implicit join notation simply lists the tables for joining, in the FROM clause of the SELECT statement, using commas to separate them. Thus it specifies a cross join, and the WHERE clause may apply additional filter predicates which function comparably to the join predicates in the explicit notation. The following example is equivalent to the previous one, but this time using implicit join notation SELECTROMemployee,department. WHEREemployee. Department. IDdepartment. Department. ID The queries given in the examples above will join the Employee and Department tables using the Department. ID column of both tables. Where the Department. ID of these tables match i. Last. Name, Department. ID and Department. Name columns from the two tables into a result row. Where the Department. ID does not match, no result row is generated. Thus the result of the execution of the query above will be Employee. Last. Name. Employee. Department. IDDepartment. Department. Name. Department. Department. IDRobinson. 34. Clerical. Jones. 33. Engineering. Smith. 34. Clerical. Heisenberg. 33. Engineering. Rafferty. 31. Sales. The employee Williams and the department Marketing do not appear in the query execution results. Neither of these has any matching rows in the other respective table Williams has no associated department, and no employee has the department ID 3. Marketing. Depending on the desired results, this behavior may be a subtle bug, which can be avoided by replacing the inner join with an outer join.
Recent Pages
- Code Free Learning Morse Software Developer
- Nero V7 10 And Up Keygen Generator
- Install Adobe Reader 9 Silently
- Tomtom Via No Maps Found After Update Firefox
- Fine Motor Skills Strengthening Activities For Elderly
- Adobe Paint Shop Cs4 Download
- Sap Download Manager Failed 400
- Symantec Antivirus For Linux Review